Mon - Fri 8:00am - 6:00pm
Give us a call:
Our Blog

By C Deselle
•
February 12, 2025
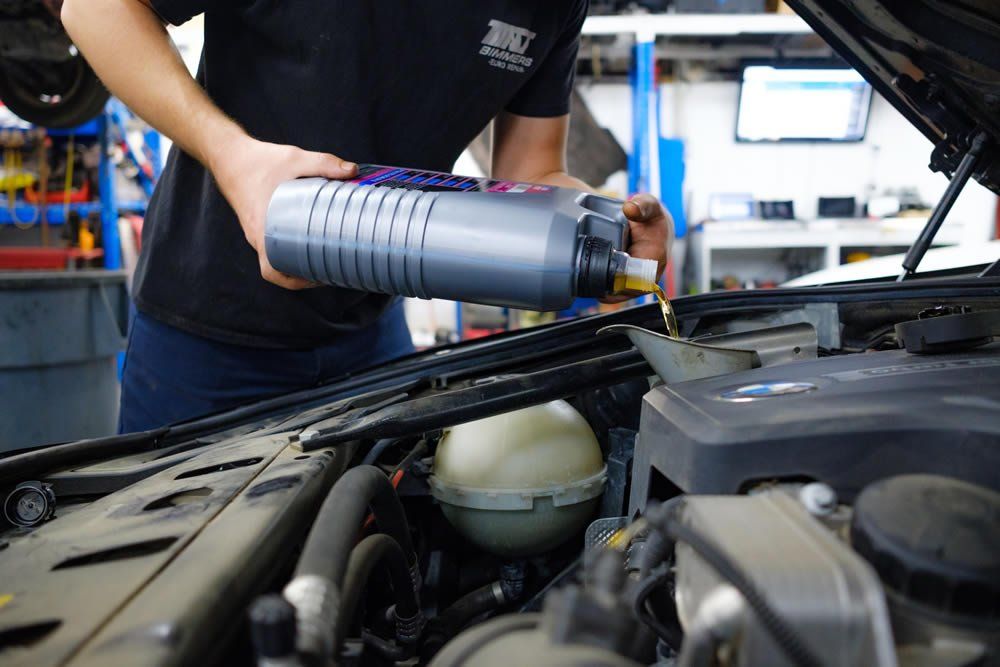
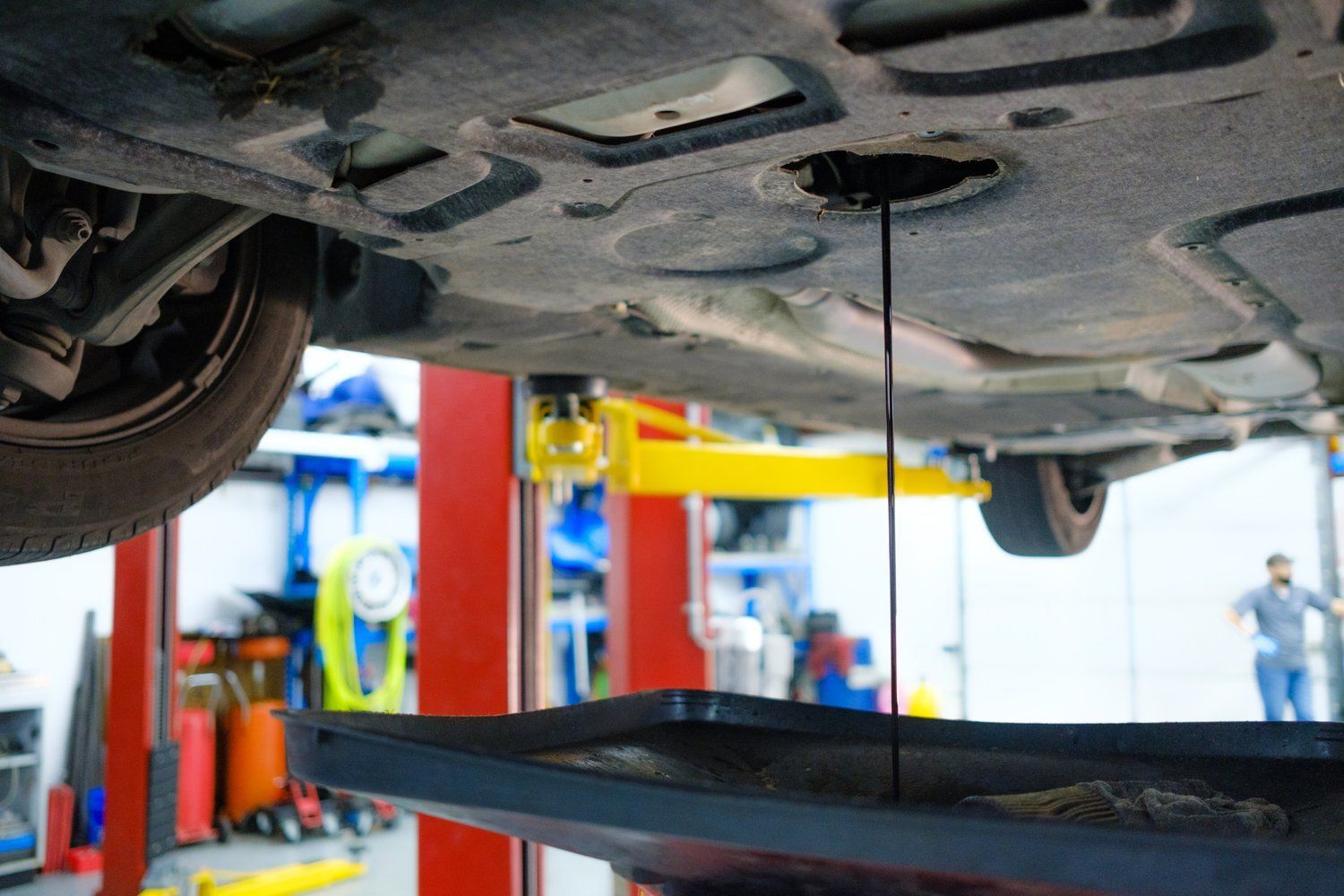
Oil leaks are one of the most common issues BMW owners encounter. While these leaks might seem like minor inconveniences, ignoring them can lead to costly repairs and potentially serious damage to your engine. At TMJ Bimmers, we’ve seen and repaired countless BMW oil leaks, and three culprits consistently top the list: valve cover leaks, oil filter housing gasket leaks, and oil pan gasket leaks. Let’s break down these issues, their causes, and how they can be resolved. 1. Valve Cover Gasket Leak What It Is: The valve cover sits on top of your BMW’s engine and seals the valve train. Over time, the gasket that seals the valve cover becomes brittle and starts to leak. This is particularly common in models like the BMW 3 Series, 5 Series, and X Series vehicles, especially those with higher mileage. Signs of a Problem: A burning oil smell due to oil dripping onto the exhaust manifold. Visible oil leaks around the top of the engine. Check engine light (CEL) due to misfires caused by oil seeping into the spark plug wells. Engine running rough or noticeable performance issues. Causes: High engine temperatures causing gasket material to degrade. Normal wear and tear due to age and usage. Improper installation or over-tightening during previous repairs. Waiting too long between oil changes; Extended oil change intervals leading to sludge buildup, which accelerates wear. Potential Consequences : If left unchecked, a valve cover gasket leak can lead to more severe problems, such as damaged ignition coils or fouled spark plugs. This can result in misfires, reduced fuel efficiency, and costly repairs. How We Fix It : At TMJ Bimmers, we replace the valve cover gasket with a high-quality OEM or aftermarket part, ensuring proper torque specifications to prevent future leaks. We also inspect the valve cover itself for cracks, which can occur on older models. After the repair, we thoroughly clean the area to remove any residual oil. 2. Oil Filter Housing Gasket Leak What It Is : The oil filter housing gasket seals the connection between the oil filter housing and the engine block. Over time, this gasket can deteriorate, leading to leaks. This issue is particularly common in turbocharged BMW engines, such as the N54 and N55. Signs of a Problem: Oil pooling near the front of the engine. Unexplained decreased oil levels between oil changes. Visible oil stains on the engine or driveway. Unusual engine noises caused by low oil pressure. Causes : Exposure to heat and pressure, which breaks down gasket material over time. Age-related wear, especially in vehicles with over 60,000 miles. Poor-quality replacement gaskets from previous repairs. Waiting too long between oil changes; Delayed oil changes causing sludge buildup around the gasket. Potential Consequences: Ignoring an oil filter housing gasket leak can cause engine components to wear prematurely. It can also lead to low oil pressure, which in extreme cases, can result in engine failure. How We Fix It: We’ll replace the failing gasket and thoroughly clean the area to ensure no residual oil remains. During the repair, we’ll inspect nearby components like the oil cooler gasket, as it’s often affected in tandem. Additionally, we check for oil contamination in the cooling system, which can occur if the issue is left unresolved for too long. 3. Oil Pan Gasket Leak What It Is: The oil pan gasket seals the oil pan to the bottom of the engine. This gasket can fail, especially in older or high-mileage BMWs. Vehicles that experience frequent stop-and-go driving or those exposed to harsh road conditions are particularly susceptible. Signs of a Problem: Oil spots on your garage floor or driveway. Visible oil dripping from the underside of the car. Low oil level warning on the dashboard. Increased oil consumption requiring frequent top-offs. Causes: Damage from road debris or impacts causing stress on the oil pan. Long-term wear and exposure to heat, which weakens gasket material. Over-tightened bolts leading to gasket compression and failure. Improper installation during previous repairs. Potential Consequences : An untreated oil pan gasket leak can lead to low oil levels, causing inadequate lubrication of engine components. Over time, this can result in excessive wear, overheating, and potentially catastrophic engine damage. How We Fix It: Replacing an oil pan gasket involves removing the oil pan, cleaning the mating surfaces, and installing a new gasket. This process requires precision and care, as improper installation can lead to further leaks. While the oil pan is off, we inspect for sludge or debris to ensure the engine stays in optimal condition. We also replace the engine oil and filter as part of the service. Why Do BMWs Experience Oil Leaks? BMWs are known for their precision engineering and high-performance engines. However, these characteristics also make them more prone to oil leaks due to: Higher operating temperatures compared to many other vehicles. The use of synthetic oil, which can expose weaknesses in gaskets over time. Complex engine designs with multiple gaskets and seals. Regular maintenance and timely repairs are key to keeping your BMW in peak condition. Why Choose TMJ Bimmers for Your BMW Repairs? Oil leaks are more than just a nuisance—they can compromise your engine’s performance and longevity. At TMJ Bimmers, we specialize in BMW maintenance and repairs, offering: Expertise : Our team is trained to diagnose and repair common BMW issues efficiently. High-Quality Parts : We use OEM and premium aftermarket parts to ensure durability and reliability. Transparent Communication : We’ll walk you through the repair process and provide clear, upfront pricing. Comprehensive Inspections : Every repair includes a thorough inspection to identify and address potential issues before they escalate. If you suspect your BMW has an oil leak, don’t wait for the problem to worsen. Contact us today at 713.384.2273 or visit tmjbimmers.com to book your appointment at our Houston shop to have your vehicle inspected. Let’s keep your BMW running smoothly and leak-free for miles to come!
TMJ Bimmers Euro Auto Repair
Mon - Fri 8:00am - 6:00pm
Payment Options







Services
List of Services
-
Air Conditioning ServiceAir Conditioning Service
-
Alignment SpecialistAlignment Specialist
-
Battery ServicingBattery Servicing
-
Brake Inspection and ServiceBrake Inspection and Service
-
Check Engine Light ServicesCheck Engine Light Services
-
Complete Computer DiagnosticsComplete Computer Diagnostics
-
Coolant Systems RepairCoolant Systems Repair
-
Differential & Transfer Case ServicingDifferential & Transfer Case Servicing
-
Electrical System RepairElectrical System Repair
-
Engine Service and RepairEngine Service and Repair
-
Muffler & Exhaust System Repair and UpgradeMuffler & Exhaust System Repair and Upgrade
-
Fuel System ServiceFuel System Service
-
Oil ChangeOil Change
-
Performance & Transmission TuningPerformance & Transmission Tuning
-
Pre-Purchase InspectionsPre-Purchase Inspections
-
Road-Force Wheel BalancingRoad-Force Wheel Balancing
-
Steering and SuspensionsSteering and Suspensions
-
Timing Chain Issues & RepairsTiming Chain Issues & Repairs
-
Transmission Repair and ServiceTransmission Repair and Service
List of Services
-
Air Conditioning ServiceAir Conditioning Service
-
Alignment SpecialistAlignment Specialist
-
Battery ServicingBattery Servicing
-
Brake Inspection and ServiceBrake Inspection and Service
-
Check Engine Light ServicesCheck Engine Light Services
-
Complete Computer DiagnosticsComplete Computer Diagnostics
-
Coolant Systems RepairCoolant Systems Repair
-
Differential & Transfer Case ServicingDifferential & Transfer Case Servicing
-
Electrical System RepairElectrical System Repair
-
Engine Service and RepairEngine Service and Repair
-
Muffler & Exhaust System Repair and UpgradeMuffler & Exhaust System Repair and Upgrade
-
Fuel System ServiceFuel System Service
-
Oil ChangeOil Change
-
Performance & Transmission TuningPerformance & Transmission Tuning
-
Pre-Purchase InspectionsPre-Purchase Inspections
-
Road-Force Wheel BalancingRoad-Force Wheel Balancing
-
Steering and SuspensionsSteering and Suspensions
-
Timing Chain Issues & RepairsTiming Chain Issues & Repairs
-
Transmission Repair and ServiceTransmission Repair and Service
Services
List of Services
-
Air Conditioning ServiceAir Conditioning Service
-
Alignment SpecialistAlignment Specialist
-
Battery ServicingBattery Servicing
-
Brake Inspection and ServiceBrake Inspection and Service
-
Check Engine Light ServicesCheck Engine Light Services
-
Complete Computer DiagnosticsComplete Computer Diagnostics
-
Coolant Systems RepairCoolant Systems Repair
-
Differential & Transfer Case ServicingDifferential & Transfer Case Servicing
-
Electrical System RepairElectrical System Repair
-
Engine Service and RepairEngine Service and Repair
List of Services
-
Air Conditioning ServiceAir Conditioning Service
-
Alignment SpecialistAlignment Specialist
-
Battery ServicingBattery Servicing
-
Brake Inspection and ServiceBrake Inspection and Service
-
Check Engine Light ServicesCheck Engine Light Services
-
Complete Computer DiagnosticsComplete Computer Diagnostics
-
Coolant Systems RepairCoolant Systems Repair
-
Differential & Transfer Case ServicingDifferential & Transfer Case Servicing
-
Electrical System RepairElectrical System Repair
-
Engine Service and RepairEngine Service and Repair
-
Fuel System ServiceFuel System Service
-
Muffler & Exhaust System Repair and UpgradeMuffler & Exhaust System Repair and Upgrade
-
Oil ChangeOil Change
-
Performance & Transmission TuningPerformance & Transmission Tuning
-
Pre-Purchase InspectionsPre-Purchase Inspections
-
Road-Force Wheel BalancingRoad-Force Wheel Balancing
-
Steering and SuspensionsSteering and Suspensions
-
Timing Chain Issues & RepairsTiming Chain Issues & Repairs
-
Transmission Repair and ServiceTransmission Repair and Service
© 2024 TMJ Bimmers Euro Auto Repair. All Rights Reserved | Website managed by Shopgenie